Exploring the Backbone of Connectivity: An In-Depth Look at Types of Premises Cabling
In the rapidly evolving landscape of information technology, the backbone of seamless connectivity within buildings is provided by premises cabling. Also known as structured cabling, this essential infrastructure serves as the circulatory system for data, voice, and multimedia transmissions. In this article, we will delve into the various types of premises cabling that form the lifeline of modern communication networks.
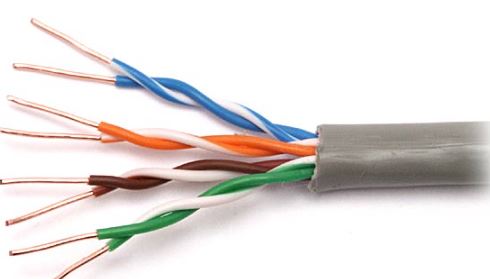
1. Twisted Pair Cabling:
- Description: Twisted pair cables are the most common type of premises cabling. They consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together, which helps reduce electromagnetic interference.
- Applications: Commonly used for Ethernet networks, telephone lines, and in various industrial applications.
- Variants: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) are the two main variants, with UTP being the more widely used.

2. Fiber Optic Cabling:
- Description: Fiber optic cables use light signals to transmit data, offering high bandwidth and long-distance capabilities. They are made of thin strands of glass or plastic.
- Applications: Ideal for high-speed data transmission, long-distance communication, and environments where electromagnetic interference is a concern.
- Variants: Single-mode fiber (SMF) for long-distance communication and multi-mode fiber (MMF) for shorter distances.

3. Coaxial Cabling:
- Description: Coaxial cables consist of a copper conductor surrounded by insulating material, a metallic shield, and an outer insulating layer. They are known for their durability and resistance to interference.
- Applications: Frequently used for cable television (CATV), broadband internet, and in networking applications.
- Variants: Different types of coaxial cables, such as RG-6 and RG-11, are designed for specific applications.

4. Power Over Ethernet (PoE):
- Description: PoE technology allows both data and electrical power to be transmitted over a single Ethernet cable. This simplifies installation and reduces the need for additional power sources.
- Applications: Widely used for devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and other networked devices.
- Benefits: Streamlines installation, reduces costs, and enhances flexibility in device placement.

5. Wireless Connectivity:
- Description: While not a traditional cabling type, wireless connectivity is an integral part of premises networking. It relies on radiofrequency signals to transmit data without the need for physical cables.
- Applications: Wi-Fi networks are prevalent in homes, offices, and public spaces, providing flexibility and mobility.
- Considerations: Bandwidth, signal strength, and security are critical factors when deploying wireless networks.